Abstract
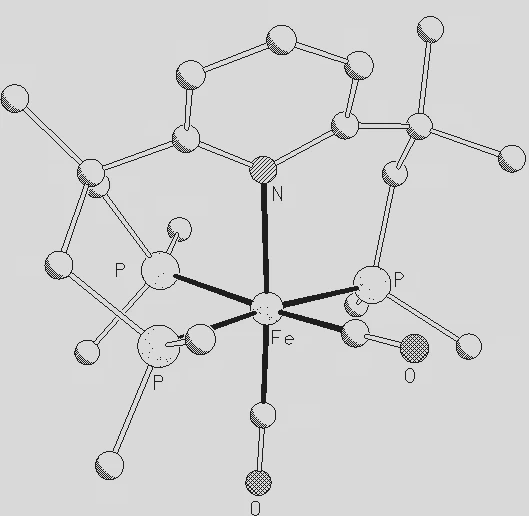
A pyridine-derived tetraphosphane ligand (donor set: NP4) has been found to undergo remarkably specific C–P bond cleavage reactions, thereby producing a ligand with an NP3 donorset. The reaction may be reversed under suitable conditions, with regeneration of the original NP4 ligand. In order to investigate the mechanism of this reaction, the NP4 donor ligand C5H4N[CMe(CH2PMe2)2][CMe2(CH2PMe2)] (11) was prepared, and its iron(II) complex 4 generated from Fe(BF4)2 · 6 H2O, with methyl diethylphosphinite (7) as an additional monodentate ligand. Ligand 11 has, in addition to the NP3 donor set, one methyl group in close contact with the iron center, reminiscent of an agostic M⋯H–C interaction. Depending on the stoichiometric amount of iron(II) salt, a side product 15 is formed, which has a diethylphosphane ligand instead of the phosphinite 7 coordinated to iron(II). While attempts to deprotonate the metal-coordinated methyl group in 4 were unsuccessful, the reaction was shown to occur in an alternative complex (18), which is similar to 4 but has a trimethylphosphane ligand instead of the phosphinite 7. The reaction of complex 15 with CO gave two different products, which were both characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. One (19) is the dicarbonyl iron(II) complex of the triphosphane ligand 11, the other (3) is the carbonyl iron(II) complex of the tetraphosphane C5H3N[CMe(CH2PMe2)2]2 (1). This suggests an intermolecular mechanism for the C–P bond formation in question.