3d- and 4d-Metal(II) Complexes of a Tris(pyridyl)ethane-Derived N₄ Ligand – A Structural Study and Reactivity Remarks
Abstract
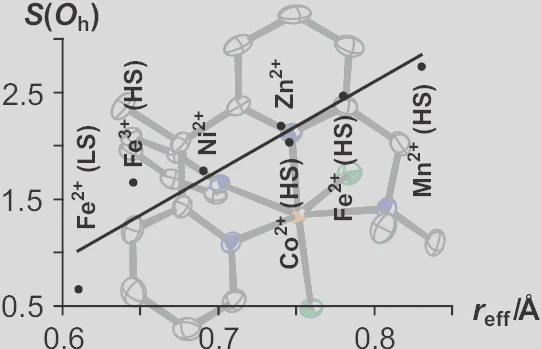
A series of complexes of the new N4 chelate ligand L (L = 1-{6-[1, 1-bis(pyridin-2-yl)ethyl]pyridin-2-yl}-N,N-dimethylmethanamine) with intermediate to late divalent transition metal ions M was obtained by the reaction between L and the respective chloride salt or similar precursor in methanol: [MCl2L] (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Zn; Ru) and [CuClL]Cl. The stereochemical characteristics of the chelate ligand were studied by means of single-crystal X-ray diffraction, and quantified on the basis of several geometric parameters, including the tetragonal distortion Σ and the continuous symmetry measure S(Oh). The overall distortion of the coordination environment is predominantly determined by the steric demand of the central ion, while electronic or other subtler influences essentially contribute to the distortion of the ligand L. Unlike similar complexes, [MnIICl2L] cannot be oxidized to a manganese(III) complex by dioxygen, hydrogen peroxide, or iodosylbenzene. In [RuIICl2L], one chlorido ligand can be exchanged against small π-accepting molecules such as acetonitrile or dinitrogen. L offers an environment ideal for small metal ions (0.4–0.6 Å), such as low-spin iron(II), which rationalizes the late onset of thermal spin crossover in the complex [FeIIL(NCS)2].