Synthesis, characterization, and crystal structure of aquabis(4,4′-dimethoxy-2,2′-bipyridine)[μ-(2𝘙,3𝘙)-tartrato(4−)]dicopper(II) octahydrate
Abstract
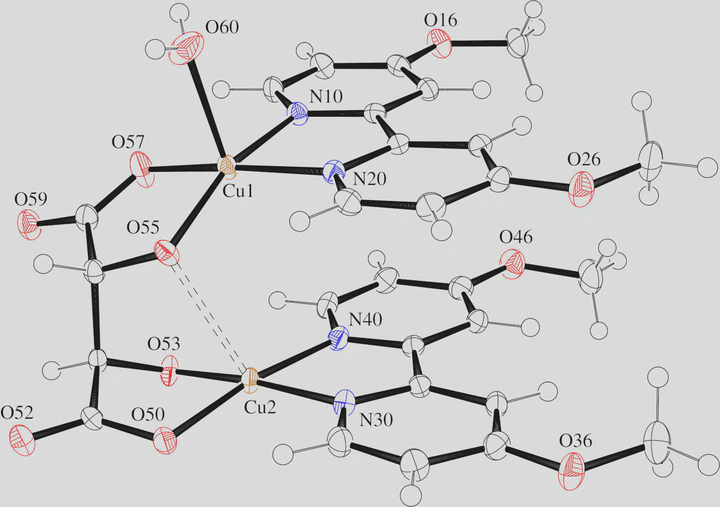
Typical electroless copper baths (ECBs), which are used to chemically deposit copper on printed circuit boards, consist of an aqueous alkali hydroxide solution, a copper(II) salt, formaldehyde as reducing agent, an l-(+)-tartrate as complexing agent, and a 2,2′-bipyridine derivative as stabilizer. Actual speciation and reactivity are, however, largely unknown. Herein, we report on the synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-1κO-bis(4,4′-dimethoxy-2,2′-bipyridine)-1κ2N,N′;2κ2N,N′-[μ-(2R,3R)-2,3-dioxidosuccinato-1κ2O2,O2:2κ2O2,O2]dicopper(II) octahydrate, [Cu2(C12H12N2O2)2(C4H2O6)(H2O)] · 8 H2O, from an ECB mock-up. The title compound crystallizes in the Sohncke group P21 with one chiral dinuclear complex and eight molecules of hydrate water in the asymmetric unit. The expected retention of the tartrato ligand’s absolute configuration was confirmed via determination of the absolute structure. The complex molecules exhibit an ansa-like structure with two planar, nearly parallel bipyridine ligands, each bound to a copper atom that is connected to the other by a bridging tartrato ‘handle’. The complex and water molecules give rise to a layered supramolecular structure dominated by alternating π stacks and hydrogen bonds. The understanding of structures ex situ is a first step on the way to prolonged stability and improved coating behavior of ECBs.